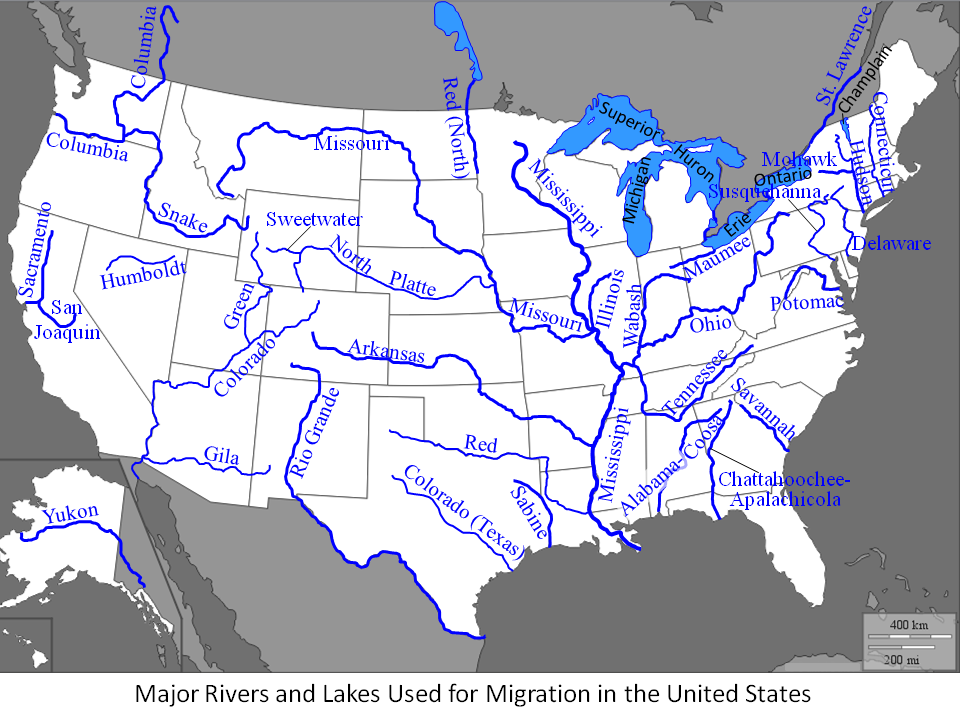
The rivers in the United States are not just waterways; they are lifelines that have shaped the nation’s history, culture, and economy. From the mighty Mississippi to the serene streams of the Pacific Northwest, these rivers serve as crucial resources for transportation, agriculture, and recreation. In this article, we will explore some of the most important rivers in the United States, their historical significance, ecological importance, and the challenges they face in the modern world.
Understanding these rivers is essential for appreciating their role in the American landscape. As we delve into the details, we will highlight key facts, figures, and the unique characteristics that make each river an integral part of the United States. This guide aims to provide you with a thorough understanding of these vital waterways and their impact on the environment and society.
Whether you are a student, a traveler, or simply curious about the natural wonders of the U.S., this article will serve as a valuable resource. By the end of our exploration, you will have a deeper appreciation for the rivers that flow through this great nation, their histories, and the vital roles they play in our lives.
Table of Contents
- 1. The Mississippi River
- 2. The Missouri River
- 3. The Colorado River
- 4. The Ohio River
- 5. The Columbia River
- 6. The Great Lakes
- 7. Challenges Facing U.S. Rivers
- 8. Conclusion
1. The Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is one of the most iconic rivers in the United States and the second-longest river in North America, stretching approximately 2,340 miles. It flows from its source at Lake Itasca in Minnesota to the Gulf of Mexico, traversing through ten states. The river has played a critical role in the economic development of the U.S., serving as a vital transportation route for goods and people.
Historical Significance
Historically, the Mississippi River has been crucial to trade and commerce. It was a key transportation route for Native Americans and later European settlers. The river’s importance continued through the 19th century as steamboats became a primary mode of transport. During the Civil War, control of the river was vital to both the Union and Confederate forces.
Ecological Importance
The Mississippi River supports a diverse ecosystem, providing habitat for various species of fish, birds, and other wildlife. Wetlands along the river are critical for flood control and water purification. The health of the river is vital for maintaining biodiversity in the region.
2. The Missouri River
The Missouri River, often considered the longest river in North America, flows 2,341 miles from its source in the Rocky Mountains of Montana to its confluence with the Mississippi River in St. Louis, Missouri. It serves as a natural boundary for several states and plays a significant role in agriculture and recreation.
Economic Role
The Missouri River is a critical waterway for agricultural transportation, allowing farmers to ship their goods to markets. Moreover, the river supports numerous hydroelectric dams, providing renewable energy to the surrounding communities.
Environmental Challenges
Despite its importance, the Missouri River faces environmental challenges, including pollution and habitat loss. Efforts are underway to restore natural habitats and improve water quality to ensure the sustainability of the river's ecosystem.
3. The Colorado River
The Colorado River is a vital water source for over 40 million people across seven states, including Arizona, California, Colorado, Nevada, New Mexico, Utah, and Wyoming. Stretching about 1,450 miles, it is known for its stunning canyons and as a key source of water in the arid Southwest.
Water Management
Water management in the Colorado River system is a complex issue due to the increasing demand for water in the region. The river is also essential for agriculture, providing irrigation to vast areas of farmland.
Recreational Activities
The Colorado River is famous for recreational activities such as white-water rafting and kayaking, attracting thousands of tourists each year to the Grand Canyon and other scenic areas.
4. The Ohio River
The Ohio River, a tributary of the Mississippi River, spans approximately 981 miles and serves as a natural border between several states, including Ohio, West Virginia, Kentucky, Indiana, and Illinois. It is an essential waterway for commerce and transportation.
Industrial Significance
The Ohio River is crucial for the transportation of coal, petroleum, and other goods. Major cities along the river, such as Cincinnati and Pittsburgh, have historically relied on the river for economic growth and industrial development.
Environmental Issues
Like many rivers, the Ohio River faces environmental challenges from pollution and habitat degradation. Initiatives are in place to monitor water quality and restore habitats to protect the river’s ecosystem.
5. The Columbia River
The Columbia River, flowing for 1,243 miles through the Pacific Northwest, is one of the most significant rivers in the region. It serves as a vital transportation route and provides hydroelectric power, irrigation, and recreational opportunities.
Hydroelectric Power
The Columbia River is home to numerous dams that produce hydroelectric power, supplying electricity to millions of people in the region. This renewable energy source plays a crucial role in the local economy.
Salmon Migration
The river is also famous for its salmon runs, which are critical to the local ecosystem and economy. Conservation efforts are ongoing to ensure the survival of salmon populations and their habitats.
6. The Great Lakes
While not rivers, the Great Lakes (Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario) are interconnected freshwater lakes that play a significant role in the ecology and economy of the United States and Canada. They provide drinking water, support fishing industries, and facilitate shipping and transportation.
Economic Impact
The Great Lakes are a major transportation route for goods, with ports that handle millions of tons of cargo annually. They also support tourism, fishing, and recreation, contributing significantly to the local economies.
Environmental Conservation
Efforts are ongoing to protect the Great Lakes from pollution, invasive species, and climate change. Organizations and governments work together to implement conservation programs and improve water quality.
7. Challenges Facing U.S. Rivers
Despite their importance, U.S. rivers face several challenges, including pollution, climate change, habitat loss, and water management issues. Addressing these challenges requires coordinated efforts from government agencies, non-profit organizations, and local communities.
Pollution and Water Quality
Many rivers are threatened by pollution from industrial runoff, agricultural practices, and urban development. Programs aimed at improving water quality and restoring habitats are essential for the health of these rivers.
Climate Change Effects
Climate change is altering precipitation patterns and water temperatures, which can affect river ecosystems and water availability. Adapting to these changes is crucial to ensuring the sustainability of U.S. rivers and their surrounding environments.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, the important rivers in the United States play a crucial role in the nation’s history, economy, and ecology. Each river has unique characteristics and challenges that require ongoing attention and conservation efforts. By understanding the significance of these waterways, we can work together to protect and preserve them for future generations.
If you found this article informative, please leave your comments below, share it with others, or explore more articles on our site to learn about the natural wonders of the United States.
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you back soon for more insightful articles!
Exploring Russell Wilson's Relationships: A Journey Through Love And Partnerships.
Everything You Need To Know About Tyreek Hill's Four Children Is Included In His Baby Mama.
Acknowledging Paula Patton's Racial Identity And Heritage.